Following on from my recent post titled “Data Locality & Why is important for vSphere DRS clusters” I would like to discuss at a high level how Write I/O works in the Nutanix Distributed File System, how the solution ensures high availability in the event of a node failure and what impact a failure has on performance.
Lets start with a typical Write operation.
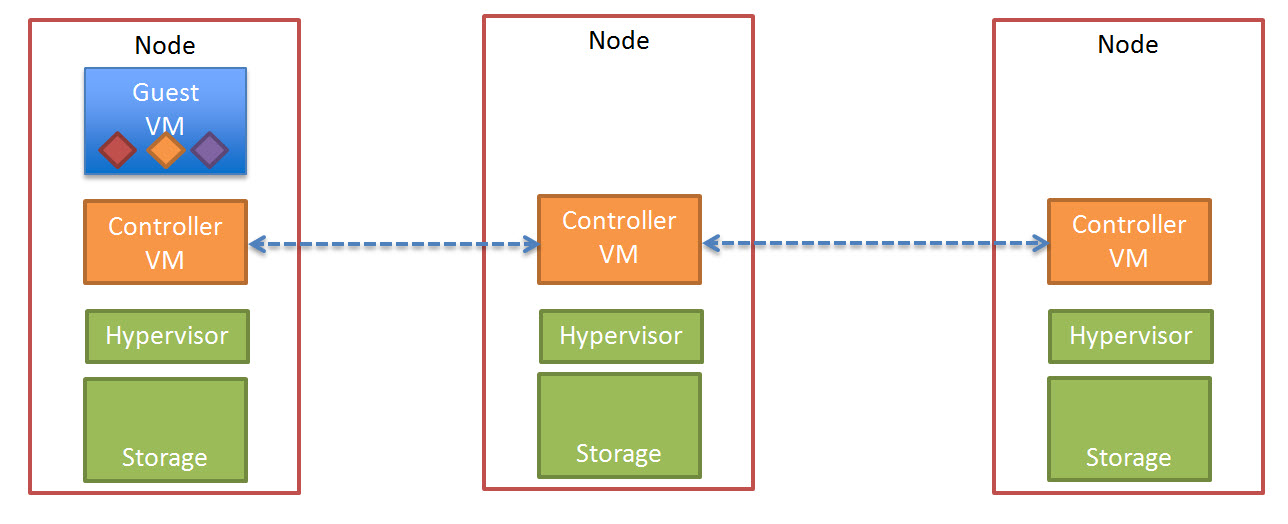
The below diagram shows a three (3) node Nutanix cluster with a Guest VM starting to perform write I/O, this is represented in a simplistic manor by the three (3) Diamonds (Red, Yellow and Purple)
The write I/O is written to the local SSD tier (as is every Write in a Nutanix environment) as shown below.
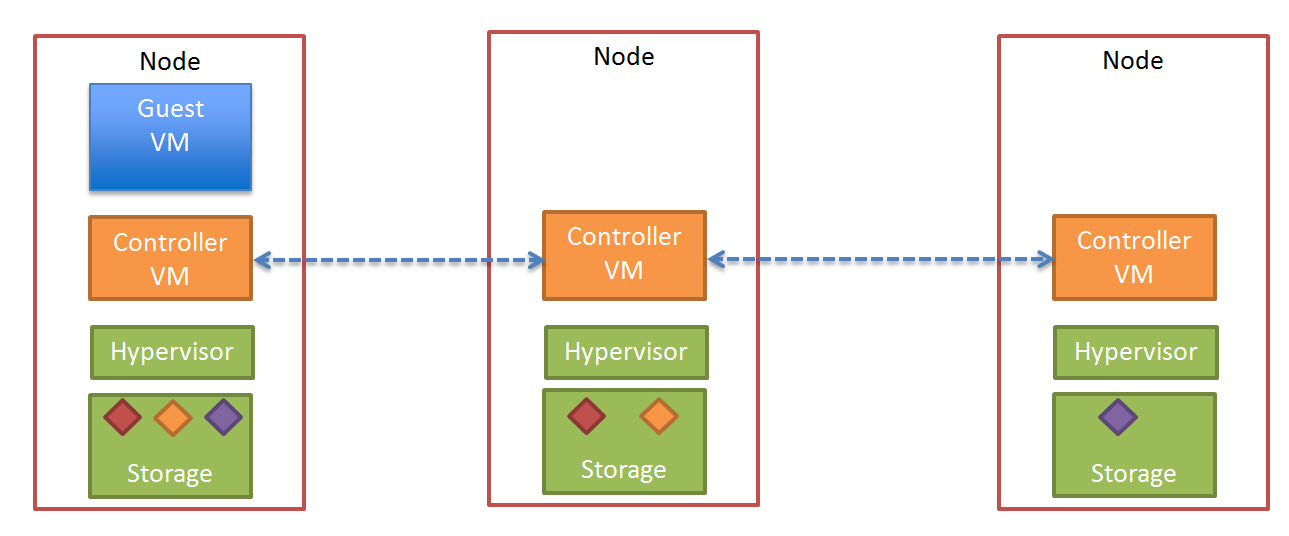
Before acknowledging the write the Nutanix Controller VM (CVM) then replicates a copy of the data across the Nutanix Distributed File System.
The below diagram illustrates what this looks like in a three node cluster.
Once the data in successfully written to other nodes within the cluster, the Write acknowledgement is given. This ensures data is consistent and always protected.
In a Nutanix cluster, as Controllers (Nutanix CVMs) are scaled linearly with the ESXi hosts, Write I/O is then spread over more controllers, reducing the chance of contention in the environment at both a storage controller and network layer as each controller shares 2 x 10Gb connections per node.
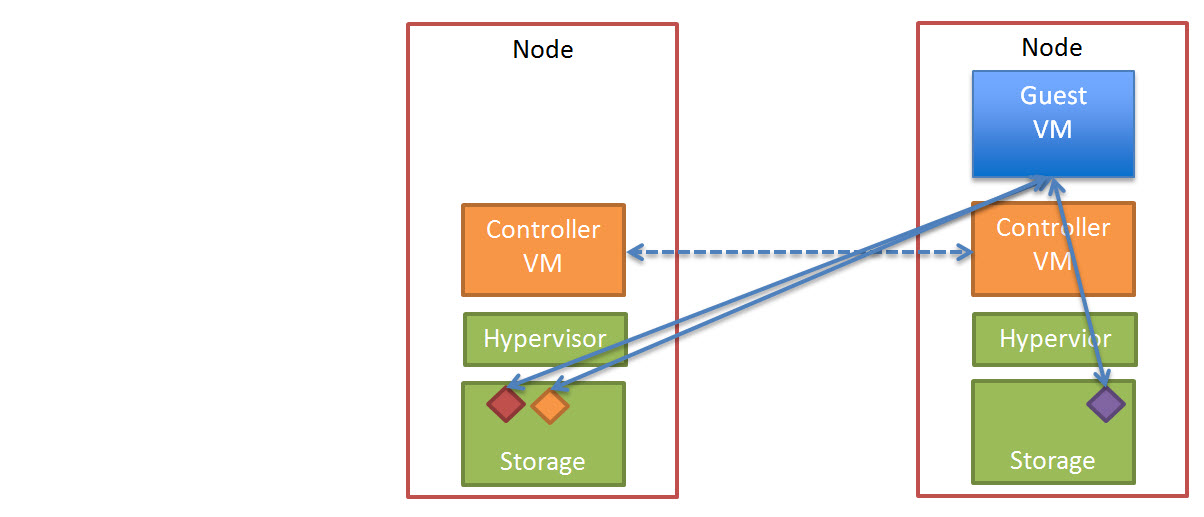
In the event of a node failure, in a vSphere cluster, HA will restart the failed VM/s onto a surviving node in the cluster.
The VM will start-up and operate as normal and where data is not local to the node (as discussed in detail in my post “Data Locality & Why is important for vSphere DRS clusters“) the data will initially be accessed over 10Gb before being replicated locally for future reads.
All future writes for the VM/s which have been restarted by HA on different nodes will perform at a similar rate (if not the same rate) as they did before the failure depending on how many nodes are in the cluster. Where the Network is not a bottleneck, there should be minimal/no difference in write performance after a node failure.
The Nutanix cluster will also detect a node has failed, and ensure two copies of all data are available, and in the above example where only one copy of the data exists, the cluster will replicate the required data to ensure High Availability (“Replication Factor” of 2) is maintained.
As this replication is done across multiple controllers and nodes, it is much faster and lower impact than a traditional RAID rebuild which most of us will be familiar with.
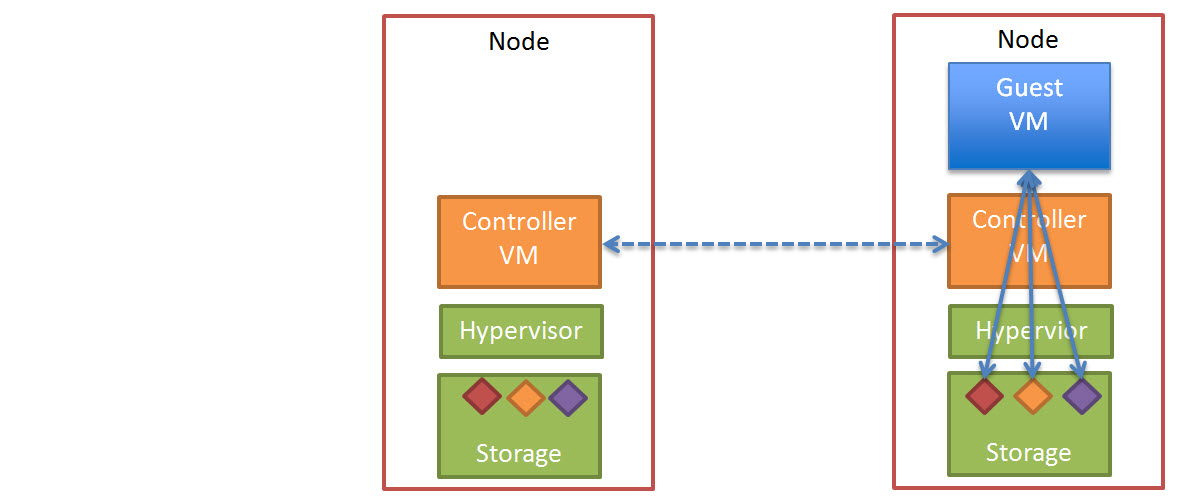
The end state of this process looks like this.
So in conclusion using a “scale-out” storage controller solution like Nutanix ensures consistent high write performance even immediately following a node failure by eliminating the requirement for RAID style rebuilds which are disk intensive and can lead to “Double Disk Failures” and data loss.
The replication of data being distributed across all nodes in the cluster ensures minimal impact to each Nutanix controller, ESXi host and the network while ensuring the data is re-protected as soon as possible.
Related Articles
1. Data Locality & Why is important for vSphere DRS clusters