In addition to Part 16 where we discussed Virtual Disk Provisioning options and recommendations, In this part we will cover how to optimally configure a Virtual Machine for an Exchange MBX/MSR workload from a virtual storage controller perspective.
Once you have made the decision on storage platform, and assuming you have chosen to use VMFS or NFS datastores (and not iSCSI in-Guest or RDMs), then this article is for you.
Virtual Machines just like physical servers, have SCSI controllers (albeit virtual) and ESXi has a number of options to choose from which include:
1. BusLogic Parallel
2. LSI Logic Parallel
3. LSI Logic SAS
4. Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI)
5. AHCI SATA Controller
By default when creating a new virtual machine the default adapter for Windows 2008 and 2012 is “LSI Logic SAS” because Windows does not have the PVSCSI driver by default.
BusLogic Parallel & LSI Logic Parallel adapters are not recommended for Windows 2008/2012 as they are legacy controllers with lower performance, as such I will not cover these in any more detail as they are irrelevant to Exchange deployments.
Instead I will cover the LSI Logic SAS , AHCI SATA Controller and Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) adapters.
Starting with LSI Logic SAS,
This is the default controller for Windows 2008/2012 VMs, as a result, it is very common to see Exchange deployments using this controller. It has good performance and works out of the box with a Windows install without requiring drivers.
Advantages:
1. The default Controller for Windows 2008/2012
2. No need for manually inserting drivers to install Windows
3. Higher performance than AHCI SATA controller
Disadvantages:
1. Lower performance than PVSCSI
2. Higher CPU overheads in Guest compared to PVSCSI
3. Higher latency than PVSCSI
4. Lower maximum number of VMDKs supported per controller (15) compared to AHCI SATA (30)
Next let’s discuss the AHCI SATA Controller.
The AHCI SATA controller is new in vSphere 5.5 and is only supported in Virtual Machines with Hardware version 10. The SATA controller can be used on its own or in addition to LSI or PVSCSI controllers to provide additional VMDKs / Capacity which increases a single VMs maximum capacity from ~3.7PB to over 11PB.
Advantages:
1. Can support 30 VMDKs per Controller (120 total) compared to 15 for LSI / PVSCSI
2. Can be used in addition to PVSCSI controllers to provide more storage performance and capacity per Exchange VM (if required)
3. High capacity supported per controller than LSI Logic / PVSCSI
Disadvantages:
1. Higher CPU utilization per IO compared to LSI / PVSCSI options
2. Lower overall performance compared to LSI and PVSCSI
3. Higher latency compared to LSI and PVSCS
And Finally the Paravirtual SCSI Controller.
The PVSCSI controller is the highest performing controller and has been supported since ESXi 4.0 and are design for high performance storage environments and are available for virtual machines running hardware version 7 and later.
Advantages:
1. Performance , Performance , Performance. Oh yeah and did I mention performance?
2. Lower Latency and Higher IOPS compared to other controllers
3. Lower CPU overhead on the Guest OS (and therefore ESXi)
4. More CPU is available for Exchange due to lower CPU overheads
Disadvantages:
1. Windows Failover Clustering is not supported, but this has no impact on MS Exchange including DAG deployments.
2. PVSCSI is not the default and requires inserting drivers into the Windows installation OR the VM to be built on LSI Logic SAS and once VMware Tools is installed, swapping to PVSCSI.
3. Lower maximum VMDKs supported per controller (15) compared to AHCI SATA (30)
Performance Comparison
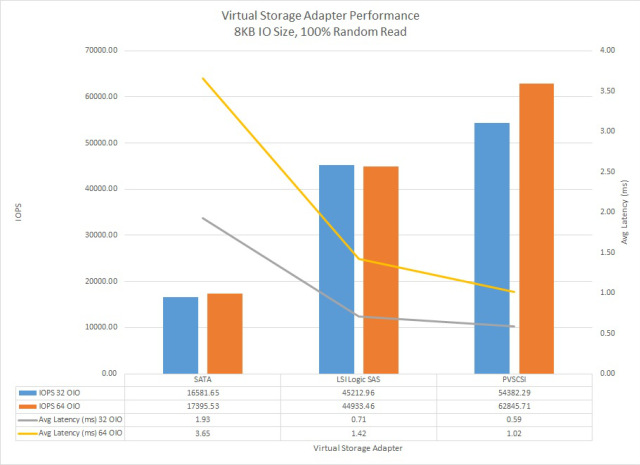
From a performance perspective, Michael Webster (VCDX#66) wrote this great post “VMware vSphere 5.5 Virtual Storage Adapter Performance” and produced the following graph showing a comparison between SATA, LSI Logic SAS and PVSCSI controllers from an IOPS, Latency perspective.
As we can see, the PVSCSI adapter has significantly lower latency and higher IOPS than the SATA and LSILogic SAS controllers even when running on the same underlying storage.
While the Microsoft Exchange team have managed to successfully reduce I/O throughout the versions (2007-2013) the performance advantages also have a positive benefit on vCPU utilization.
Michael’s post states:
It (PVSCSI Controller) also had the lowest CPU usage. During the 32 OIO test SATA showed 52% CPU utilization vs 45% for LSI Logic SAS and 33% for PVSCSI.
What this means is less CPU utilization is used for I/O and lower average latency means more CPU is available for MS Exchange along with less CPU WAIT time (where the CPU is waiting for IO to complete before continuing). This means your onto a winner especially considering Exchange 2013 is very CPU intensive.
Which Controller should be used for Exchange VMs?
VMware have published the KB article “Do I choose the PVSCSI or LSI Logic virtual adapter on ESX\ESXi 4.0 for non-IO intensive workloads? (1017652)” which in summary explains:
The test results show that PVSCSI is better than LSI Logic, except under one condition–the virtual machine is performing less than 2,000 IOPS and issuing greater than 4 outstanding I/Os. This issue is fixed in vSphere 4.1 and later version, so that the PVSCSI virtual adapter can be used with good performance, even under this condition.
As the one caveat prior to vSphere 4.1 where LSI Logic can outperform PVSCSI, there are no significant downsides to using the PVSCSI compared to LSI as such, I recommend always using (multiple) PVSCSI adapters.
Now that we have decided on the PVSCSI adapter, what’s next?
As with physical servers, Virtual SCSI controllers including PVSCSI have their limits in terms of performance and scalability. To ensure maximum scalability, performance and low latency, multiple PVSCSI adapters should be used with all VMDKs evenly spread over the PVSCSI adapters as recommended in Part 11.
To do this, when adding a VMDK to the Exchange VM, ensure you select a different SCSI controller (which are created automatically on demand) by using the drop down box “Virtual Device Node” and selecting for example SCSI (1:0) as shown below.
For subsequent VMDKs you must then select SCSI (2:0) as shown below.
And then SCSI (3:0)
For the forth VMDK, you then select SCSI (0:1) because SCSI (0:0) is taken by the VMDK used for the guest OS.
Repeat the above process until you have sufficient VMDKs for your Exchange server VM.
The following illustrates my recommended configuration showing how to configure a VM supporting 8 database drives and 8 log drives.
The above configuration will ensure maximum storage performance and can be expanded in the same configuration to support more than 3 times the number of databases + logs shown above and as such it is suitable for even very large (scale-up) Exchange MBX/MSR VMs.
For example, if each VMDK in the above configuration was just 4TB in size it would give you 64TB usable capacity and the VM can be scaled more than 3x the number of VMDKs.
Note: VMDKs can scale to 62TB (from vSphere 5.5) each although this may result in reduced performance.
TIP: Don’t forget to spread VMDKs evenly across datastores as per the recommendation in Part 11.
Recommendations for Exchange VM Storage Configuration:
1. Use multiple Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) Adapters.
2. Use one VMDK per Database or Logs
3. Spread VMDKs evenly across multiple PVSCSI adapters
4. Spread VMDKs evenly across multiple datastores when using VMFS datastores
5. Spread VMDKs evenly across multiple datastores when using NFS datastores ensuring NFS datastores are served via multiple NAS controllers
6. Use more VMDKs as opposed to fewer larger VMDKs
7. Format NTFS volumes with an Allocation Unit Size of 64k
8. Keep it simple, do not mix virtual SCSI controller types.
Back to the Index of How to successfully Virtualize MS Exchange.